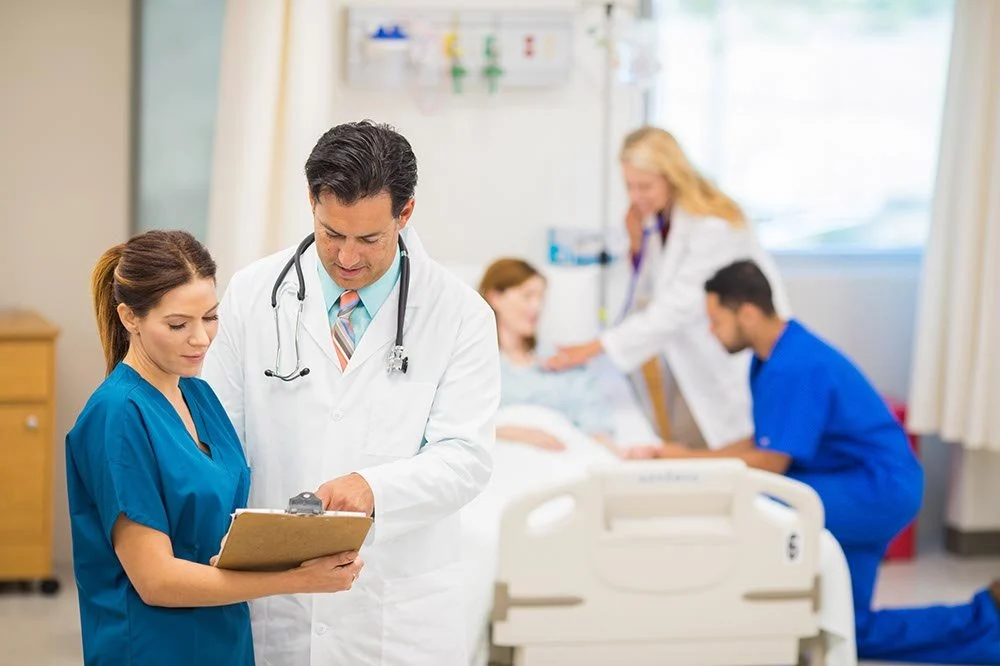
Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) is at the forefront. They provide complete care to diverse groups. The boom of medical info and tech makes it crucial for FNPs to rely on evidence-based practice (EBP). EBP ensures quality and effective patient care.
But what exactly does mastering EBP entail for FNPs, and how can they seamlessly integrate it into their daily routines? This blog post covers all these questions and more.
Read on to learn more about the FNP mastery.
What is Evidence-Based Practice?
At its core, evidence-based practice is the careful use of the best current evidence. It is used to make decisions about patient care. EBP combines clinical expertise, patient values, and the best research.
It puts them into the decision process. For FNPs, this means staying updated with the latest studies. They must add the findings to their practice to improve patient outcomes.
The Importance of EBP in Healthcare
The significance of EBP in healthcare cannot be overstated. It connects research and patient care. It makes sure that treatments are based on the best evidence.
This approach improves patient outcomes. It also boosts the credibility and reliability of healthcare providers.
Clinical Expertise Meets Research
FNPs bring a wealth of clinical experience to the table. This experience plus the latest research makes a powerful mix. It can revolutionize patient care.
Clinical expertise provides intuition and insight. They are needed to understand research and use it in the real world.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes
Research has shown that EBP leads to better care. It also leads to better patient outcomes and more efficient practices.
Following evidence-based guidelines can help FNPs cut the rate of adverse events. It can also improve treatment protocols. It ensures that patient care is effective and fast.
The Pillars of Evidence-Based Practice in FNP
To truly master EBP, FNPs need to understand its foundational pillars. These pillars are the building blocks of EBP. They guide practitioners in their quest for excellence.
Best Research Evidence
The first pillar of EBP is the integration of the best available research evidence. This involves a thorough review of scientific studies.
It looks at clinical trials and meta-analyses to find the best treatments and interventions. FNPs keep up with recent research, regularly refreshing their knowledge base.
Clinical Expertise
Clinical expertise is the second pillar. It highlights the importance of experience and intuition in patient care.
FNPs use their clinical skills to interpret and apply research findings. They tailor interventions to meet each patient’s unique needs.
Patient Values and Preferences
The third pillar emphasizes the importance of patient values. It stresses their role in decision-making.
FNPs must consider patients’ cultural, social, and personal values when recommending treatments. Ensuring that care is patient-centered and respectful of individual preferences.
Continuous Improvement
The final pillar is the commitment to continuous improvement. EBP is a dynamic process that requires ongoing learning and adaptation. They must refine their skills and assess their interventions.
Overcoming Barriers to EBP
While the benefits of EBP are clear, implementing it in practice can be challenging. FNPs may encounter several barriers that hinder their ability to adopt evidence-based principles.
Lack of Time
One of the most common barriers to EBP is the lack of time. FNPs often have busy schedules and may struggle to find time to search for and appraise evidence.
To overcome this barrier, FNPs can set aside time for research. They can also work with colleagues and use evidence-based resources.
Limited Access to Resources
Limited access to resources can also pose a challenge. FNPs work in places with few resources. They may struggle to access the latest research and evidence-based guidelines.
To address this issue, FNPs can use online databases. They can also join professional organizations and seek partnerships with academic institutions.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is another barrier that can impede the adoption of EBP. Some FNPs may be reluctant to change their practice based on new evidence.
To overcome this barrier, FNPs can get more education. They can join the best fnp programs and they can foster a culture of curiosity and openness to new ideas.
The Role of Technology in EBP
Technology plays a crucial role in facilitating the implementation of EBP. Technology provides FNPs with tools.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs offer a centralized platform for storing and accessing patient information. They let FNPs track patient outcomes.
They can check treatment progress and spot trends. These trends inform evidence-based interventions.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
CDSS are digital tools that provide real-time evidence-based recommendations to FNPs. The systems analyze patient data.
They generate custom suggestions for diagnosis, treatment, and management. This helps FNPs make informed decisions at the point of care.
Online Databases and Journals
Online databases and journals are useful. They help you access the latest research and evidence-based guidelines. FNPs can use platforms such as PubMed, Cochrane Library, and CINAHL to stay updated on new findings and advancements in healthcare.
The Future of EBP in FNP
As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of EBP in FNP practice will become increasingly important. Emerging trends and advancements in technology are shaping the future of evidence-based healthcare.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is an emerging trend that tailors treatments to individual patient characteristics. EBP is crucial to personalized medicine. It provides the evidence to develop targeted therapies and interventions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI could revolutionize EBP. It can analyze vast data and find insights. These insights inform clinical decision-making. Algorithms powered by AI can identify patterns.
They can predict outcomes and suggest evidence-based interventions. This enhances the precision and effectiveness of patient care.
Interprofessional Collaboration
Interprofessional collaboration is essential for the successful implementation of EBP. FNPs must work closely with other healthcare professionals, including:
- physicians
- pharmacists
- allied health practitioners
This is to ensure a coordinated and comprehensive approach to patient care.
Continuous Education and Training
Continuous education and training are vital for keeping FNPs updated on the latest evidence and best practices. A significant portion of the AANP FNP practice questions emphasizes the application of evidence-based guidelines in clinical scenarios. These questions challenge candidates. They must use the newest research and clinical advice in their decisions.
Understanding the FNP Mastery
Evidence-based practice is a fundamental component of FNP mastery. It empowers FNPs to deliver high-quality, patient-centered care that is grounded in the best available evidence. By understanding the pillars of EBP, overcoming barriers, leveraging technology, and staying updated on emerging trends, FNPs can master the art of evidence-based practice and provide exceptional care to their patients.
For more helpful tips, check out the rest of our site today!
Stay in touch to get more updates & news on Buzz Feed!