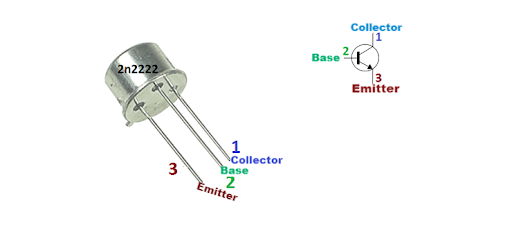
2N2222
In the world of electronics, understanding component pinouts is crucial for building circuits and ensuring proper connections. In this article, we’ll dive into two widely-used components: the 2N2222 transistor and VGA connector. Whether you’re a hobbyist, engineer, or student, knowing the pinouts of these components will significantly enhance your understanding and ability to troubleshoot circuits.
What is the 2N2222 Transistor?
The 2N2222 is a popular NPN transistor used in various electronic applications. It acts as a switch or amplifier and is ideal for low to moderate power applications. The 2N2222 transistor is widely used in digital circuits, amplifiers, and switching circuits.
The 2N2222 has three pins, each with a specific function:
- Pin 1: Collector (C)
- This pin is connected to the load in a circuit. It is responsible for carrying the current from the external circuit.
- Pin 2: Base (B)
- The base pin controls the current flowing between the collector and the emitter. It is the input for the transistor.
- Pin 3: Emitter (E)
- The emitter pin is the output of the transistor. It sends the current to the ground (or negative side of the circuit).
2N2222 Circuit Applications
- Switching Circuits: The 2N2222 is frequently used in low-power switching circuits, allowing control of larger current flows with a low current input.
- Amplifiers: In analog circuits, the 2N2222 can amplify weak signals to a higher voltage.
- Signal Processing: It is commonly used in applications like signal modulation and amplification in radios and audio systems.
What is VGA?
VGA (Video Graphics Array) is an older but widely used video display standard that allows the connection of a computer to a monitor or projector. It is an analog video output standard, which typically uses a 15-pin connector for transmitting video signals.
The VGA connector features 15 pins, arranged in three rows. Here’s a breakdown of the pinout:
- Pin 1: Red
- Transmits the red component of the video signal.
- Pin 2: Green
- Transmits the green component of the video signal.
- Pin 3: Blue
- Transmits the blue component of the video signal.
- Pin 4: Monitor ID
- Reserved for monitor identification. Typically unused in most applications.
- Pin 5: Ground
- Provides a common ground for all signals.
- Pin 6: Red Ground
- Ground for the red signal to ensure proper voltage levels.
- Pin 7: Green Ground
- Ground for the green signal.
- Pin 8: Blue Ground
- Ground for the blue signal.
- Pin 9: Key (No Pin)
- Empty pin to prevent misconnecting the VGA cable.
- Pin 10: Sync Ground
- Provides ground for synchronization signals.
- Pin 11: Horizontal Sync
- Sends horizontal synchronization information to the display.
- Pin 12: Vertical Sync
- Sends vertical synchronization information to the display.
- Pin 13: Monitor ID
- Another monitor ID pin, used for extended features.
- Pin 14: Reserved
- Reserved for potential future use.
- Pin 15: Monitor ID
- Another monitor identification pin.
VGA Pinout Applications
- Computer Monitors: VGA connectors are commonly used to link desktop computers and monitors.
- Projectors: Many projectors, especially older models, still utilize VGA inputs for video display.
- Older Gaming Consoles: VGA connectors were also common in older gaming systems and arcade machines.
Why Is Knowing Pinout Important?
Understanding the pinouts of both the 2N2222 transistor and VGA connector can help you design and troubleshoot circuits more effectively. Whether you’re working on a transistor circuit or connecting a VGA-compatible display, proper knowledge of the pinouts ensures correct wiring and prevents circuit failures.
Applications in Modern Electronics
- 2N2222 Pinout: Used for creating signal amplifiers, building power supply circuits, and controlling small motors in various applications, including robotics.
- VGA Pinout: While VGA is an older standard, it still finds applications in industrial equipment, older televisions, and legacy computer systems.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored the essential pinouts of the 2N2222 transistor and VGA connector. By understanding how to use these pinouts in your circuits, you can improve your design and troubleshooting skills. Whether you’re connecting a VGA monitor or building a transistor-based circuit, this knowledge is fundamental to successful project development.
Related Articles:
- How to Use 2N2222 Transistor in Circuit Design
- Differences Between VGA and HDMI Pinouts
- The Basics of NPN and PNP Transistors
Want to Learn More?
For more detailed information on electronic components and circuit design, check out our other articles on PCB manufacturing, transistor applications, and video connectors.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Buzz Feed!






