Aging is a natural process that brings a variety of changes to the body, and one of the most common issues faced by many as they grow older is joint pain. This discomfort can significantly affect your quality of life, making everyday activities challenging. Understanding how to effectively reduce joint pain is essential for maintaining mobility and enjoying life to the fullest. In this article, we’ll explore various strategies for managing joint pain as you age, focusing on lifestyle changes, exercise, nutrition, and medical options.
Understanding Joint Pain
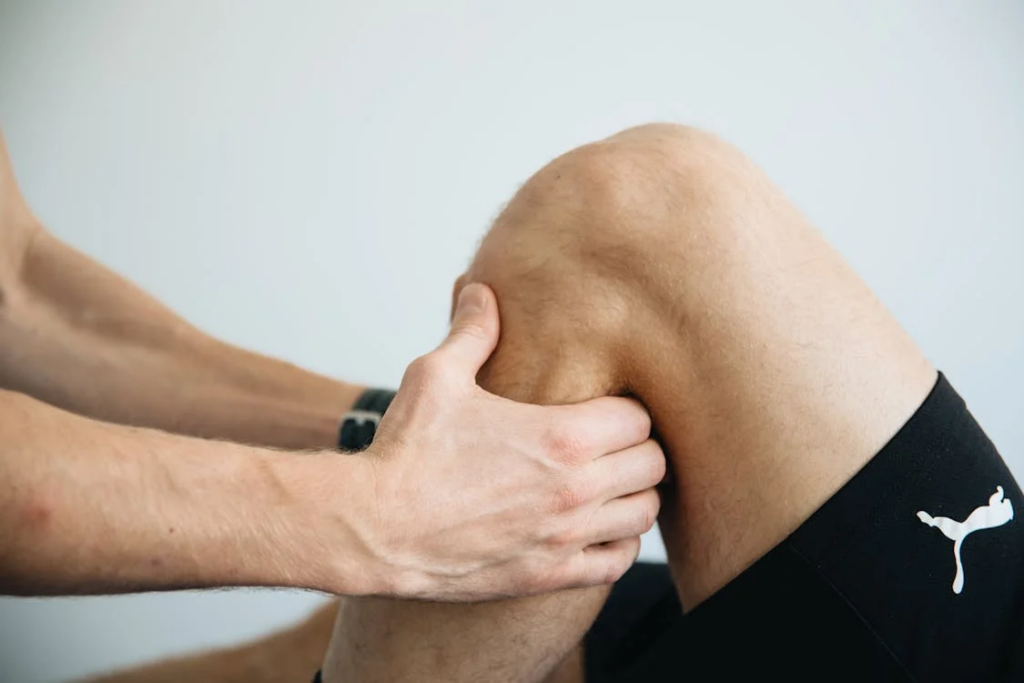
Joint pain can arise from a range of conditions, with osteoarthritis being the most prevalent among older adults. This degenerative joint disease occurs when cartilage—the protective tissue at the ends of bones—wears down over time. Other causes of joint pain may include rheumatoid arthritis, injuries, gout, and inflammation. Recognizing the source of your pain is vital for effective management.
Lifestyle Changes for Joint Health
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts additional stress on your joints, particularly those in the lower body, such as the knees and hips. Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate some of this pressure and reduce pain. Incorporate a balanced diet rich in whole foods—fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains—to help manage your weight effectively.
Stay Hydrated
Hydration is often overlooked when discussing joint health. Water plays a critical role in maintaining joint lubrication. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, or more if you are active. Proper hydration can help keep joints functioning optimally and may reduce stiffness.
The Role of Exercise
Low-Impact Activities
Regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to reduce joint pain. Engaging in low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, and walking can strengthen the muscles around your joints without causing additional stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week.
Flexibility and Strength Training
Incorporating flexibility and strength training exercises into your routine is also beneficial. Stretching improves flexibility, which can help prevent injuries and alleviate stiffness. Strength training helps build muscle support around joints, reducing strain during movement. Consult with a fitness professional or physical therapist to create a personalized exercise plan that suits your needs.
Pain Management Techniques
Medications
For many individuals, over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen) can provide effective relief for joint pain. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication. In some cases, doctors may prescribe specific medications, including Malegra Pro or Sildalist, to help manage pain or address related issues. Always use medications under medical supervision to ensure safety and efficacy.
Hot and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to affected joints can offer immediate relief. Heat therapy, such as warm baths or heating pads, can help relax muscles and improve blood flow. Cold therapy, using ice packs or cold compresses, can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. Alternating between hot and cold treatments can also provide substantial relief.
Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist can be an invaluable step in managing joint pain. They can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around your joints, improve flexibility, and educate you on proper body mechanics to prevent further injury.
Nutritional Considerations
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help reduce joint pain. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), walnuts, and flaxseeds, can decrease inflammation. Additionally, foods like turmeric and ginger have natural anti-inflammatory properties. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to promote overall health.
Supplements
Some supplements may provide additional relief for joint pain. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate are popular options that some studies suggest may help support joint health. Omega-3 supplements, such as fish oil, can also help reduce inflammation. However, consult with your healthcare provider before starting any supplements to ensure they are appropriate for you.
Alternative Therapies
Consider exploring alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, or chiropractic care. These therapies can complement traditional treatments and may offer relief from joint pain. Mindfulness practices like yoga and meditation can also help manage pain by reducing stress and improving mental well-being.
Staying Active and Positive
While managing joint pain can be challenging, maintaining an active lifestyle is crucial. Engaging in social activities, pursuing hobbies, and staying connected with friends and family can improve your mental health and overall well-being. Join support groups or community classes focused on fitness or health to share experiences and gain motivation.
Conclusion
Reducing joint pain as you age is achievable through a combination of lifestyle changes, exercise, pain management techniques, and nutritional adjustments. It’s essential to take proactive steps to maintain your joint health and overall quality of life. If you experience persistent joint pain, consult with a healthcare provider to explore your options. With the right approach, you can continue to enjoy the activities you love and live a fulfilling life despite the challenges that aging may bring.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Buzz Feed!